Guide language: the connotation of green lighting contains high efficiency energy saving, environmental protection, safety, comfortable 4 index, indispensable. Efficient energy saving means that it can obtain sufficient illumination by consuming less electricity, thus significantly reducing the emission of atmospheric pollutants in power plants and achieving environmental protection.
1. Greenlights, green lighting
The connotation of green lighting includes four indicators of high efficiency, energy saving, environmental protection, safety and comfort. Efficient energy saving means that it can obtain sufficient illumination by consuming less electricity, thus significantly reducing the emission of atmospheric pollutants in power plants and achieving environmental protection. Safe and comfortable means that the light is clear, soft and does not produce uv, glare and other harmful light, does not produce light pollution.
2. Visual task visualtask
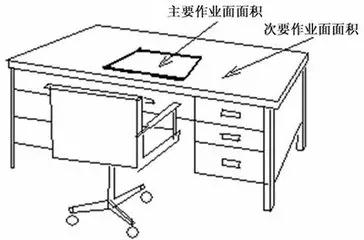
In work and activity, the observation of the details and objectives presented in the background. Visual work is divided into primary visual and secondary visual tasks, depending on the area of visual retention.
Figure: the lamp main irradiation area is the main visual work, diffuse light around the secondary visual work
3. Luminous flux luminousflux
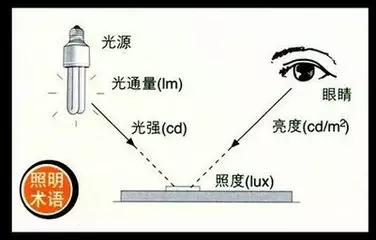
Light metric derived from radiation to the standard photometric observer. The unit is lumen (lm), 1lm=1cd/ 1sr. For bright vision:
Type in the
D Φ e (lambda)/d lambda - the spectral distribution of radiation flux;
Nu (lambda) - spectral light (apparent) efficiency;
Km- the maximum value of the spectral (visual) efficiency of radiation. The unit is lumen per watt (lm/W). In monochromatic radiation, the Km value under the visual condition is 683lm/W (lambda m= 555nm).
Diagram: schematic diagram of luminous flux principle
4. Luminous intensity luminousintensity
The luminous intensity of light in a given direction is the light within the solid Angle in the direction of the yuan d Ω transmission flux d Φ divided by the solid Angle of the quotient, namely the luminous flux per unit solid Angle. The unit is kendra (CD), LCD = 1lm/sr.
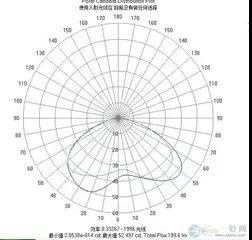
Figure: distribution of luminous intensity
5. Luminance brightness
By formula L = Φ/d2 (dA, cosine theta d Ω) defined amount, unit is candela per square meter (CD/m2).
Type in the
D Φ - from a given point of yuan transmission and contain the given direction within the solid Angle d Ω spread of luminous flux (lm);
DA - including a given point of the beam cross-sectional area (㎡);
Theta -- the Angle between the normal of the beam cross section and the direction of the beam.
6. Light illuminance
The intensity of illumination refers to the amount of energy in the unit area that receives the visible light, or as the illumination, the unit Lux (Lux or Lx). A physical term used to indicate the intensity of light and the amount of surface area being illuminated.
Calculation method for the luminous flux incident on the bin contains point d Φ divided by the surface of the shang dA yuan area, unit for lux (lx), 1 lx = 1 lx / ㎡.
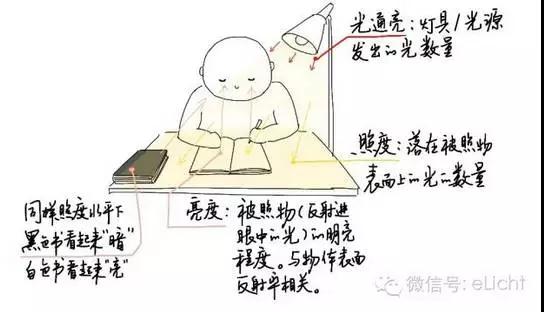
Many students are confused with brightness and brightness. How to distinguish them? A picture tells you!
Figure: the generation and distinction of brightness and illumination. LOGO (hand-painted)
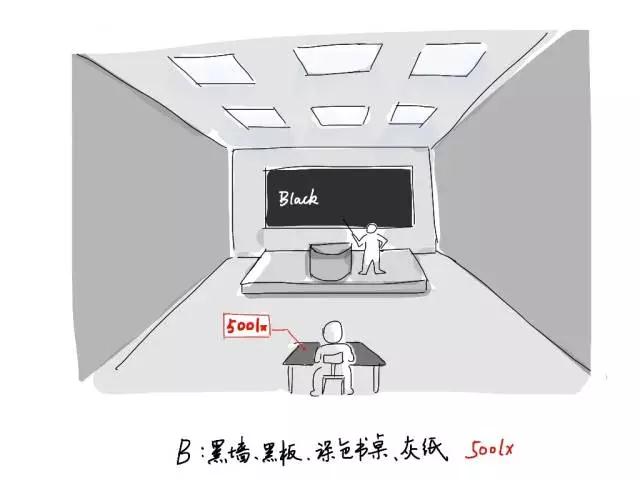
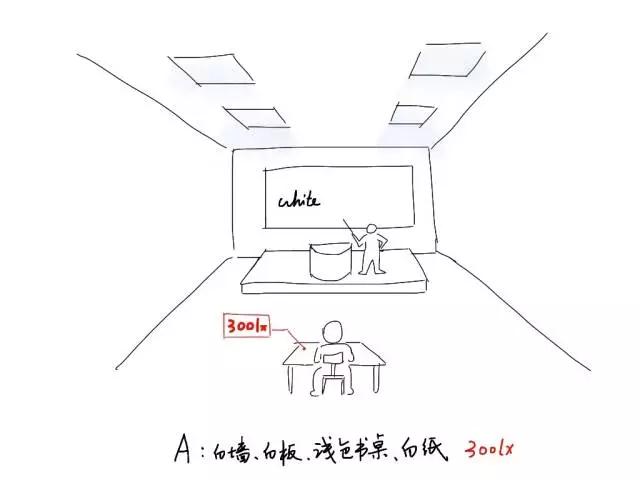
So, the same space, different basic hues have different requirements for illumination
Graph: the classroom of white basic tone is the requirement of illuminance. (LEGO hand-painted)
Graph: the requirement of the classroom of black basic tone to illuminance. (LEGO hand-painted)
Averageilluminance, averageilluminance
Very simple, is the illumination of the light source to specify the average value of the illuminance on the surface.
8. To maintain the average illuminance maintainedaverageilluminance
The average illumination on the surface must not be lower than this value. It is a time when the lighting fixtures must be maintained, in the rules
The average illumination on the surface.
9. Reference plane referenceplane
A plane that measures or specifies illumination.
10. Workingplane
The plane of work on its surface.
11. Maintenancefactor maintenancefactor
Lighting in use after a certain period, in the average illuminance on the surface or the average brightness and the device on the new clothes in the same conditions in the same surface of the ratio of the average illuminance or average brightness.
Illumination on the surface of the lighting system and after the use, operation is lower, is due to the light source itself luminous flux output decreases, lamps and lanterns of material aging light transmittance and reflectance of the decline and environmental dust pollution on the surface of lamps and lanterns and indoor lamps and lanterns light output efficiency and to reduce the surface reflectivity of indoor wait for a reason. (PS: in the light loss in a number of factors, some can be replaced by clean lamps and lanterns and indoor surface or maintenance way to recover, such as the light source is called recoverable loss factors, and other factors, are involved in lamps and lanterns, ballast deterioration or loss, unless the replacement lamps and lanterns, otherwise can't recover, called unrecoverable loss factor light.)
12. General lighting generallighting
Also known as "background illumination", or "ambient lighting", is the foundation of a lighting planning, is full of the directional lighting of the room, the room for the space of all activities to create a common enough lighting.
13. General lighting localizedgenerallighting
The evolution of general lighting, for a particular area, such as the location of work, is designed to illuminate the general lighting of the region in different illumination.
14. Local lighting locallighting
In order to meet the special needs of certain parts of the room, the lighting mode of lighting lamps is set in a certain range.
Lighting fixtures are usually installed above the work surface. Local lighting mode can obtain higher illumination in local range with smaller light source power, and it is easy to adjust and change the direction of light. Local lighting method commonly used in the following situations, such as local needs to have a higher intensity of illumination, due to the shade and make the general lighting illuminate within certain range, need to reduce the work zone reflected glare, in order to strengthen a direction of illumination in order to enhance building texture. However, only local lighting can cause visual fatigue during long working hours.
15. Mixed lighting mixedlighting
Lighting with general lighting and local lighting. Used to create a more flexible lighting effect.
16. Accent lighting accentlighting
Also known as "decorative lighting", to improve the illumination of a designated area or target, it is more illuminating than the surrounding area. It is usually used to emphasize specific parts or furnishings of space, such as architectural elements, architecture, clothing, collectibles, decorations and works of art, museum artifacts, etc.
17. Normal lighting normallighting
Lighting used in normal circumstances.
18. Emergency lighting emergencylighting
Lighting enabled by the failure of normal lighting. Emergency lighting includes evacuation lighting, safe lighting and spare lighting. One of the most common things in life is the ubiquitous emergency lights and safe evacuation lights.
19. Evacuation lighting evacuationlighting
Emergency lighting used to ensure that evacuation channels are effectively identified and used.
20. Safety lighting safetylighting
Used to ensure emergency lighting for personnel in potential danger.
21. Standby lighting stand-bylighting
Emergency lighting to ensure continued or temporary continuation of normal activities.
22. Stroboscopic effect stroboscopiceffect
Under the light of a certain frequency change, the observation of object motion shows different phenomena than the actual motion.
23. Light-emitting diode (LED) light lightemittingdioamp
A semiconductor device that is made of solid luminescence as a light source for lighting.
24. The intensity distribution distributionofluminousintensity
Using a curve or table to indicate the luminous intensity value of a light source or lamp in all directions of space, also known as light distribution.
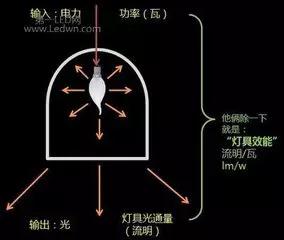
The luminous efficiency luminousefficacyofalightsource 25. The light source
The light flux emitted by the light source divided by the power of the light source. The unit is lumen per watt (lm/W).
26. Luminaire efficiency luminaireefficiency
The ratio of the total luminous flux emitted by the luminaire to the total luminous flux emitted by all the light sources in the lamp is also called the light output ratio of the lamp.
27. Luminaireefficacy for luminaire luminaire
The ratio of the total luminous flux emitted by the lamp to the power input under the prescribed conditions of use. The unit is lumen per watt (lm/W).
28. The intensity of illumination evenness uniformityratioofilluminance
The ratio of the minimum illumination on the surface to the average illuminance is U0.
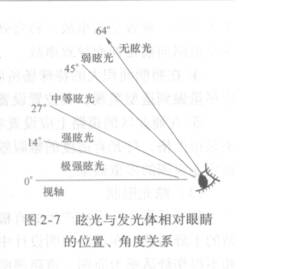
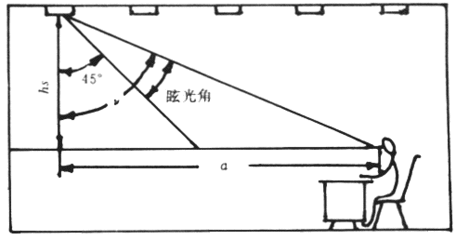
29. Glare glare
A visual phenomenon that causes discomfort or decreases the ability to observe a detail or target due to the incongruity of the brightness distribution or the range of brightness in the field of view.
30. Direct glare directglare
The glare from the field of vision, especially the luminosity that exists near the line of sight.
31. Discomfort glare discomfortglare
Produces discomfort, but does not necessarily reduce the visibility of visual objects.
32. Uniform glare value unifiedglarerating(UGR)
The international lighting commission (CIE) is used to measure the psychological parameters of the light emitted by lighting devices in a visual environment to cause discomfort to the human eye.
33. Glare value glarerating(GR)
The international lighting council (CIE) is used to measure the psychological parameters of the subjective response to the discomfort of human eyes by measuring the lighting of stadiums and other outdoor venues.
The reflection is glarebyreflection
A glare caused by reflection in the field of view, especially the glare of reflection from the direction of view.
35. The light screen reflects veilingreflection
The mirror reflection of the visual object, which reduces the contrast of the visual object, so that it is difficult to see the detail in part or all.
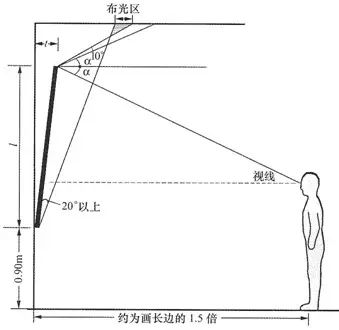
36. The lamps and lanterns of shielding Angle shieldingangleofluminaire
The Angle between the plane of the light source and the line of sight that happens to be invisible.
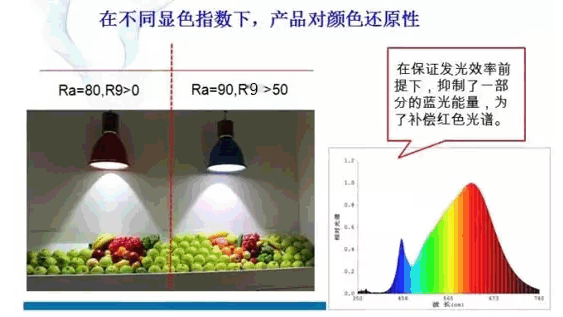
37. Colorable colourrendering
Compared with reference standard light source, the light source shows the color of the object.
38. Color index colourrenderingindex
A measure of the color of the light source. The color of the object under the light source is the same as the color of the object under the reference standard.
39. The general generalcolourrenderingindex color rendering index
The average value of the color index of the 1-8 standard color samples specified by the international lighting commission (CIE). An index of significant color, which is Ra.
40. Special specialcolourrenderingindex color rendering index
The light source is an index of the color sample of the 9th to 15 standard color samples selected by the international lighting commission (CIE). The symbol is Ri.
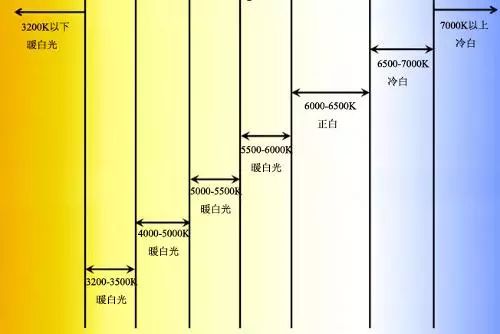
41. The colour temperature colourtmeperature
When the color of the light source is completely identical to that of the black body at a certain temperature, the absolute temperature of the black body is the color temperature of the light source. Also called "chromaticity". The units are open (K).
42. The correlated color temperature correlatedcolourtemperature
When illuminant chromaticity point not on the planckian locus, and light color with a temperature of blackbody chromaticity closest to the absolute temperature of the blackbody correlated color temperature of light, or correlated color temperature. The symbol is Tcp, and the unit is open (K).
43. Chromaticitytolerances
The deviation of the nominal color of light source and light source in a batch of light source is represented by the color matching standard deviation.
44. Luminousfluxmaintenance for luminousfluxmaintenance
The ratio of the luminous flux to the initial luminous flux after a given ignition time.
Reflection is more than reflectance
The ratio of radiant flux or luminous flux to the radiation flux or flux of the incident radiation in a given state of the incident radiation, the polarization state and the geometry distribution.
46. Lighting powerdensity lightingpowerdensity(LPD)
Per unit area of the general lighting installation (including power source, ballast or transformer auxiliary power devices etc.), the unit of watts per square meter (W / ㎡).
47. Chamber index roomindex
The numerical value of the geometry of a room or place is twice the size of a room or place and the difference between the height of the installation height and the height of the working face.
48. Annual exposure of annuallightingexposure
The value of an object's annual cumulative acceptance of light, and the product of the acceptance of an object as the product of the cumulative hour of the year, is the annual lux hour (lx· h/a).
49. Color vector graph ColorVector
The tm-30-15 provides a color vector map while providing dual indicators, which can provide a more intuitive message to indicate the color shift and saturation of various colors.
50. Colorless ColorVector
Color purity is auxiliary, said at the time of dominant wavelength describe color in percentage, defined as a chromaticity coordinates and E light source under test (namely can white illuminant, can white is above the white dots position) shown in the chromaticity coordinates of the straight line distance, and E light source to the piece of dominant wavelength spectrum under test track (SpectralLocus) the percentage of the chromaticity coordinates, distance, the higher the purity, on behalf of the under test pieces of the chromaticity coordinates, the more close to its the main wavelength spectrum of color.
The original image of the image, the softer color
The color of the color is 80% and the color is bright and moving
The color is less than 80% and the color is darker
Source: cnledw2013